
In this article we'll talk about JSON Web Tokens (JWT).JSON web tokens are a standard and secure way to transmit information between two parties on the internet as a JSON object.
Think of a JWT as similar to a cookie that is not saved in the browser.
If someone signs into our application with their credentials, after we verify the credentials are correct and the user exists, we can generate a JWT and send it back to the client.
The next time a request is made, the JWT is sent back to our server, where we can verify it and allow access to our resources.
JWT are basically a hashed and encoded string that is passed between the server and the client in an API transaction.
Structure of a JWT
JWT are structured as one string of characters made up of three components: a header, a payload and a signature.
The header specifies the algorithm used to create the hash.
The payload contains information our application is interested in, like what the token is for, possible user information, and so on.
The signature is a security check that validates that the token has not been modified since it was first issued.
You can use an online tool such as JWT.io to view and decode a JSON web token. This tool lets you visualize the various parts that compose a JWT: header in red, payload in purple, and signature in blue.
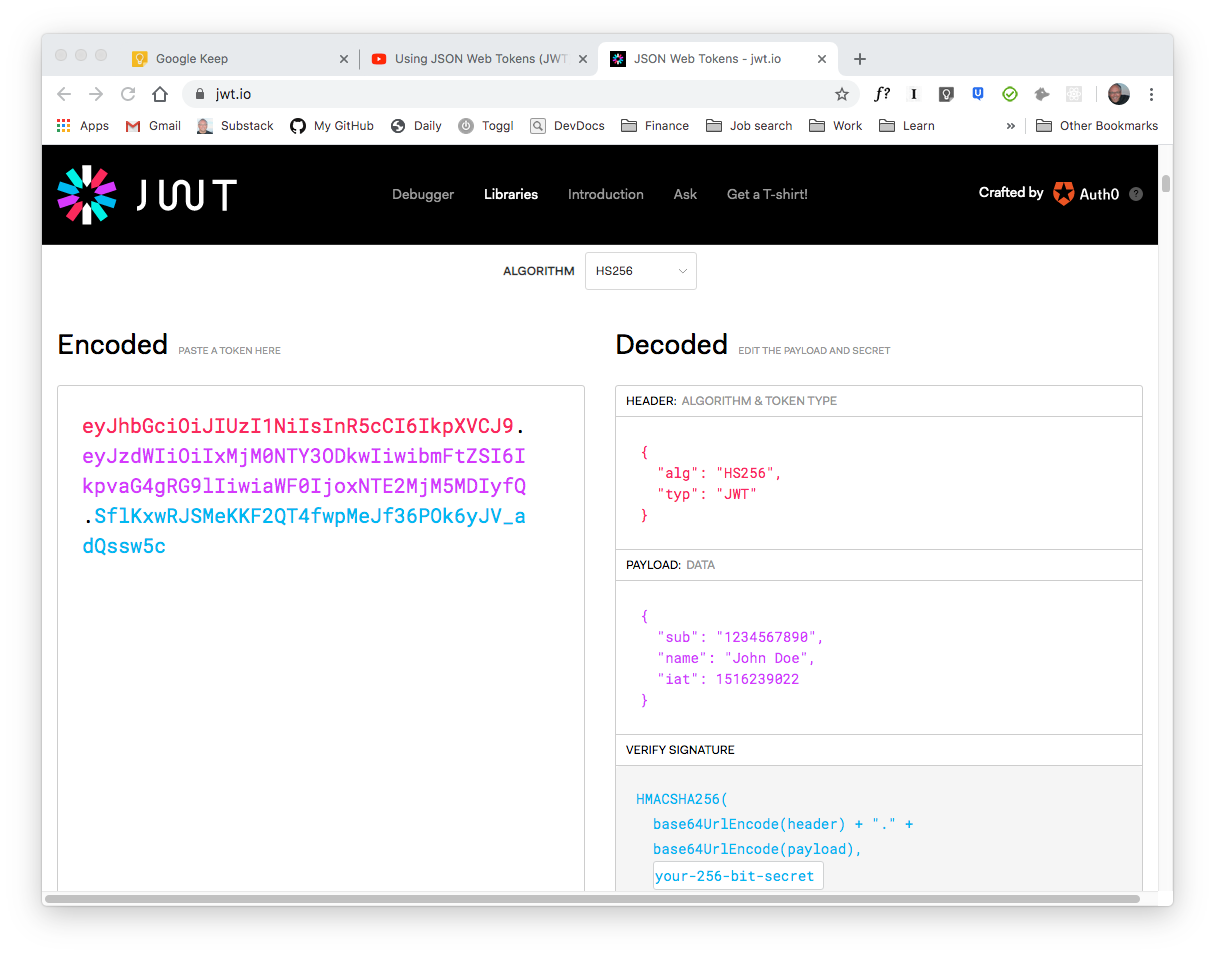
Header and payload encode the actual data in the web token, while the purpose of the signature is to verify that header and payload have not been tampered with.
When our server creates a JWT it provides a secret string that is used to hash the token.
Our server will take the header and the payload, add the secret and from this combination it will create the signature hash. The signature is then attached to the end of the token.
Later, when we receive the token back from the client, our server takes the header and payload from the received token, combines them with the secret that is stored on our server and generates a signature, the same way it was generated in the first place.
If the generated signature matches the one coming from the token, the token is considered valid and access is granted.
But if the two signatures don't match, we know that the token has been modified along the way so we refuse access to the client that made the request.
One of the reasons tokens are popular is because they also work well with third party authentication system providers.
To generate and manage web tokens in our Express application we use a library called jsonwebtoken, available as a Node module.
We install the library in the usual way:
yarn add jsonwebtokenWith this we are ready to write some code and see some examples of how to use JWT in our application. We'll do that in the following articles.
Did you like this article? Share it with your friends.
I write daily about front-end and back-end web technologies.
You can receive all my articles in your inbox by subscribing to my newsletter. Just click the button below. No spam, just good, useful content. Guaranteed!
Follow me on Twitter


